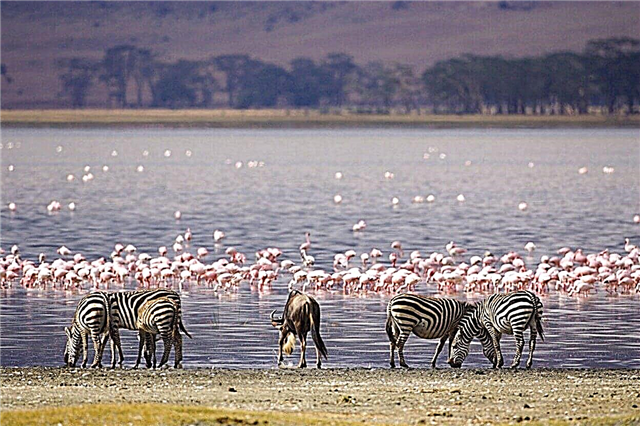
In order to preserve the diversity of flora and fauna on the territory of Russia, a nature reserve was created throughout the country in different years. These are protected zones, designed to protect not the entire territory as a whole (which is how they differ from reserves), but its individual parts: some plants, animals, or small ecosystems. Various kinds of research are carried out here, as well as work to increase populations.
Regional and federal reserves differ from each other. Depending on the structure and type, reserves can be either independent or part of state reserves or national parks of Russia. On the territory of the reserves, economic activity is partially limited. Only that which cannot affect the environment is allowed. Ecological tourism is also acceptable; often you need a pass for a visit.
List of interesting nature reserves in Russia
South Kamchatka
It was founded in 1983 on the territory of the Kamchatka Territory and occupies 322 thousand hectares, including the water area. The river network and coastline make it an interesting tourist destination. The fish spawning area attracts bears; they can be observed at a distance. There are three volcanoes, the second largest lake in the Kuril region, stone birch forests, Vestnik Bay, Utashud Island and other natural objects.

Kizhi
It is located in the Republic of Karelia on an area of 50 thousand hectares since 1989. The reserve has complex tasks, including the protection of not only rare species and landscapes, but also historical sites, for example, sites of the Mesolithic and Neolithic times. Natural objects of increased importance: the Kizhi skerries are a unique complex and nesting places for birds, including waterfowl.

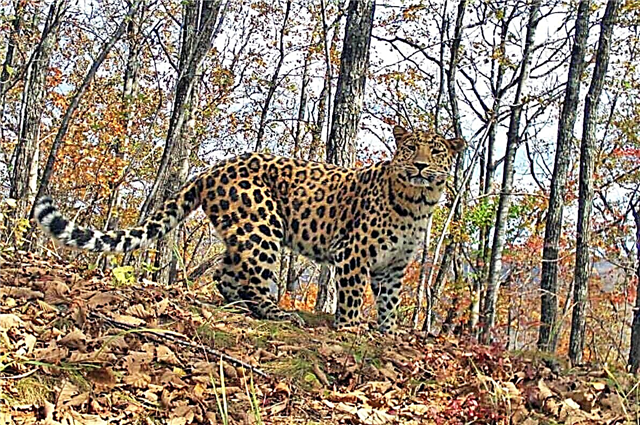
Leopard print
Located on the border with China in the Primorsky Territory. Year of foundation - 2008. Area - 169.5 thousand hectares. Combined from two reserves. Considerable efforts are being made to preserve the population: it is necessary not only to ensure the safety of the species, but also to prevent the environment from deteriorating so that the Far Eastern leopards do not leave these lands. 4 years after its foundation, it was declared part of the Land of the Leopard Nature Reserve.

Small Kuriles
Location - Sakhalin Region, time of foundation - 1982, area - 45 thousand hectares, including water area. The reserve is based on islands, so the composition of flora and fauna is not uniform everywhere. Key natural sites: Tserkovnaya Bay, where seabirds nest, Cape End of the World - a seal rookery, larch grove. Japan claims this territory, not recognizing it as Russian.

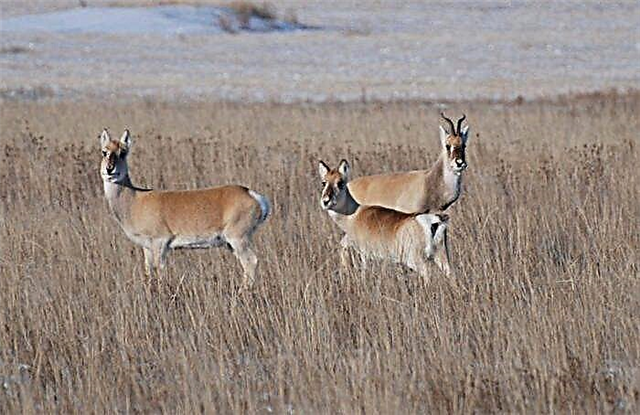
Gazelle valley
Created in 2011 in the Trans-Baikal Territory. The area is slightly less than 214 thousand hectares. The terrain is steppe, there are two rivers that almost dry up during dry periods. The most protected species are Mongolian gazelles. It is an important object for animal migrations. The Daursky Nature Reserve is located nearby. Tourism is informative here: the staff of the reserve not only conducts research, but also educates travelers.

Agrakhansky
It has been part of the Republic of Dagestan since 1983. The area is 39 thousand hectares. Belongs to the Terek delta. The area can be considered an oasis, as there are dry plains around. One of the goals of its creation is an attempt to preserve the population of commercial species, practically exterminated by decades of uncontrolled hunting and fishing. The unique ecosystem was formed largely thanks to the abundant aquatic vegetation.

Altacheysky
It was put on maps in 1984 and occupies 78 thousand hectares in the Republic of Buryatia. Since 2011, part of the "Baikalsky Reserve". One of the directions of tourism is photography, which attracts guests even from abroad. Red deer, roe deer, capercaillie and other inhabitants of the reserve get into the lens of successful travelers. In addition to natural beauty, historical monuments are also protected here, for example, dolmens and sanctuaries of ancient people.

Krasny Yar
It is located in the Irkutsk region on an area of more than 49 thousand hectares since 2000. Forty years before that, it was a hunting reserve. Now a special environmental management system has been introduced: every action is accountable. The main goal is to protect ungulates (red deer, elk, roe deer) and their habitat. Forests, mostly mixed, cover almost the entire territory. They are the backbone of the ecosystem of the entire region.

Voronezh
Belongs to the territory of the region of the same name since 1958. The area is 23 thousand hectares. You can rest here, but in specially designated places. Any activity that can negatively affect the environment or interfere with the usual rhythm of life of animals is prohibited. Natural objects: Turtle Lake with a population of marsh turtle, Chervlyony Bor, where the pine forest is about 140 years old, Maklok spring and others.

Dautsky
Founded in 1986 in Karachay-Cherkessia and occupies about 75 thousand hectares. Two types of terrain coexist and complement each other: dense forests and alpine meadows. The reserve is focused on a zoological profile, so that representatives of the fauna are protected to a greater extent, and any kind of hunting is prohibited. To visit you need to get a pass. The Teberda Nature Reserve is located nearby.

Mshinskoe swamp
It has existed since 1982 on more than 60 thousand hectares in the Leningrad Region. Most attention is paid to lakes and swamps. Any activity that can change the ecosystem is prohibited, however, the advancement of civilization towards a protected area also harms nature. It is not easy to get here: there are only a few paved paths. Tourist tours are conducted on an ongoing basis.

Oldzhikansky
It was founded in 1988 in the Khabarovsk Territory. The area is more than 59 thousand hectares. Resting and feeding place for migratory birds. It is part of the Komsomolsky reserve. There was a Stalinist women's camp, from which only ruins remained. A unique phenomenon of the reserve is a lake in a lake. On the largest lake in the region, Chukchagir, there are islands, and in one of them there is a small and almost perfect lake Krugloye.

Belozersky
Year of origin - 1986, area - more than 17 thousand hectares, location - Tyumen region. The purpose of creation is the reproduction of game animals, an increase in their number. Lake Svetloye is an intermediate stop during the flight of the population of the white crane. The study of local living creatures continues. For some types of repair work and construction, you need to obtain a permit, the rest is prohibited.

Tlyaratinsky
It appeared in Dagestan in 1986 on an area of more than 83 thousand hectares. It is part of the Dagestansky reserve. Predators and hunting species live nearby, which does not prevent the reserve staff from monitoring the populations. When visiting, you must have your passport with you, since the zone belongs to the border. Attraction - "The Plateau of Falling Lakes" - several reservoirs with an emerald smooth surface.

Tseysky
It was founded in North Ossetia in 1958 and covers more than 29 thousand hectares. Here they are actively building sites for feeding animals and birds, as well as making artificial nests to make life easier for birds. Architectural landmarks: the villages of Dzivgis, Urikau and Dallagkau. Oriental beech belongs to rare species, and beech-gab forest is a valuable natural object.

Elizarovsky
Year of foundation - 1982, location - Khanty-Mansi Autonomous Okrug, area - 76 thousand hectares. "Upper Dvuobie" is a wetland of international importance. It is considered a subdivision of the Malaya Sosyeva nature reserve. The Ob floodplain is a place of nesting and molting of waterfowl. Their migration routes pass here as well. The reserve has a wide range of purposes, it is universal in terms of species protection.

Eloguisky
It extends over 747 thousand hectares of the Krasnoyarsk Territory. The documents on his education were signed in 1987. The purpose of creation is to protect the ecosystems of the middle taiga.The population of the local subspecies of wild reindeer is recovering. It is also a sable reserve. In addition to protecting nature, there is a need to preserve the cultural heritage of the indigenous peoples of the north, including the Khanty.

Kirzinsky
Occupies more than 119 thousand hectares in the Novosibirsk region since 1958. Conservation and research activities are mostly related to wetlands and birds that are characteristic of this type of terrain. Significant natural objects: Lake Chany - salty, drainless, the largest in Western Siberia, the "Shchuchye Lakes" area - a tract of international importance, Kazantsevsky Cape - a natural monument.

Purinsky
It was founded in 1988 on 787 thousand hectares of the Krasnoyarsk Territory. It is part of the "Mesopotamia and the valleys of the Pura and Mokorrito rivers" - a wetland of international importance. Environmental research and monitoring are part of the responsibilities of the reserve staff. It is important for animals as a transit point during migrations, therefore, in some periods, the livestock significantly increases.

Klyazminsky
Refers to two regions at once: Vladimir and Ivanovo. Featured on maps since 1978. The area is about 21 thousand hectares. Key objects: Lake Krashcha with its legend about the "floating island", the Uvod river, popular with tourists who love rafting, Lake Velikoe, which is heavily overgrown by the coast. One of the most protected species is desman. The site of an ancient man of the Upper Paleolithic era was discovered.

Verkhne-Kondinsky
It exists in the Khanty-Mansiysk Autonomous Okrug on an area of 241 thousand hectares since 1971. Plays an important role in the protection of beavers. Swamp complexes and lichen forests are unique zones that have become protected areas. The local beauty attracts artists and photographers. Access for them, naturalists and other travelers is not limited by time, but you need to get a pass. Nearby is the Malaya Sosva nature reserve.

Tofalar
Founded in 1988 on an area of over 132 thousand hectares in the Irkutsk region. The territory is covered with taiga forests, they look especially picturesque on the slopes of the Sayan Mountains. Protected species are fur animals, including sable, and the snow leopard, which are monitored by the reserve staff in order to keep track of the population. Natural attractions - Kosurgashev glacier and Medvezhye lake.

Kunovatsky
It was founded in 1985 in the Yamalo-Nenets Autonomous Okrug. The area is 220 thousand hectares. Divided into 2 clusters. The location in the floodplains of the Ob and the Small Ob has formed a certain ecosystem here with a focus on flora and fauna, gravitating towards water. There are shallow rivers, lakes and swamps. Fish are also specially protected species, so fishing is prohibited in almost the entire territory.

Mekletinsky
Located in Kalmykia on 102 thousand hectares since 1988. Local lakes are mostly small, which is due to the arid climate. The largest lake is Koltan-Nur. Saigas have chosen this territory for breeding: here their young are born and grow stronger. There is a highway nearby, which has a negative impact on the environment. The second big problem is poaching.

Murmansk tundra
Belongs to the territory of the Murmansk region since 1988. The area is about 295 thousand hectares. An important natural object is the tundra and the hunting fauna that inhabits it. The workers of the reserve are trying to make the local environment even more attractive for some species, thereby stimulating their reproduction and excluding migration. The key zones are the Iokanga River delta, as well as the Yenozero basin on the southern side.

Kurgalsky
Appeared on the maps of the Leningrad Region since 2000. The area is 60 thousand hectares. Tourists can use transport, but the parking areas are strictly regulated. Key objects - Kader swamp, relic dunes. Ringed seals can be found along the coast. People come here by car, and the surroundings are often examined from rowing or inflatable boats. Due to the laying of the Nord Stream 2, the reserve is under threat.

Muromsky
Located in the Vladimir region. Founded in 1968 and covers an area of more than 56 thousand hectares. The main protected species is the desman. A local natural attraction is Lake Visha, which has been declared a natural monument. A bison is depicted on the welcome sign. Its population here is impressive, from here even small herds were taken to other areas for breeding.

Remdovsky
Refers to the territory of the Pskov region. Formed in 1985. The area is over 74 thousand hectares. Initially, it served as a hunting fauna reserve. Cranberry bogs "Turinskoe", "Krivoy moh" and others are natural monuments. The reserve includes a group of large islands. It is also a historical site, as the Battle of the Ice took place here. Great tourist potential.

Sochi
It has been located in the Krasnodar Territory since 1993 on an area of more than 48 thousand hectares. The contact of different types of landscapes is unique and needs to be protected. Since the region is flooded with tourists, there are risks associated with environmental pollution. Sometimes they get into the reserve by accident and do not know how to behave correctly, therefore, bypassing the territory is an important duty of employees.

Sarpinsky
It was formed on the territory of Kalmykia in 1987. The area is about 195 thousand hectares. Environmental education is one of the goals. Steppe endemics are especially protected here. There are hunting grounds nearby, but the boundaries are clearly drawn. It is easy to get to the Sarpinskaya lowland, where the reserve is located, you may need a pass, but not in all seasons.

Ingush
Belongs to the territory of Ingushetia since 1971. The area is over 70 thousand hectares. There are monuments of history and culture, protected along with nature. Especially valuable are: bezoar goat, chamois, tur and others. The terrain is heterogeneous: highlands, alpine meadows, forests, deltas of several rivers. This diversity influences the emergence of specific ecosystems, opening up additional opportunities for researchers.

Kabansky
Occupies more than 12 thousand hectares on the lands of Buryatia since 1974. One of the main goals is to protect bird nests and other bird habitats. It also skates the species that live near Lake Baikal. Wetlands are included in the list of important internationally. The admission to the territory must be obtained from the administration of the reserve. Vehicles are prohibited. It is under the control of the Baikal Nature Reserve.

Tsasucheisky Bor
It appeared in 1988 on more than 57 thousand hectares of the Chita region. Created primarily for the preservation of the relict plant community. Particularly valuable species: black stork (4-5 pairs) and Siberian roe deer (the highest population density in Siberia). While staying here, you need to follow a large set of rules and coordinate your actions with the administration of the Daursky reserve.

Udyl
Founded in 1988. The area is more than 100 thousand hectares on the territory of the Khabarovsk Territory. The fauna and part of the flora have been well studied, and work with the relief, climate and other details continues. The local wetlands are of international importance. Valuable species: dry borer, Steller's sea eagle, fish owl and others. Since 2009, the reserve has been part of the Komsomolsky reserve.

Severozemelsky
Located in the Krasnoyarsk Territory since 1996. The area is over 421 thousand hectares. It is divided into 4 zones: "Akhmatov Bay", "Domashny Island", "Matusevich Fjord", "Peninsula of the Paris Commune". Each has its own characteristics, including relief, but the order of nature management is the same for everyone. The territory can be visited, but be guided by the memos available along the entire perimeter of the reserve.